General Overview
Coronaviruses cause acute and chronic respiratory, enteric, and central nervous system (CNS) diseases in humans and many species of animals. Coronaviruses are divided into three groups based on the genome sequences, including SARS-CoV (a member of group II) as well as murine hepatitis virus (MHV), bovine coronavirus, porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (HEV), equine coronavirus, and human coronavirues OC43 and NL63, which also cause respiratory infections. SARS-CoV, the causal pathogen of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), caused a large outbreak of this severe pneumonia occurred in Hong Kong in 2003 and rapidly spread throughout the world. SARS-CoV can infect and replicate in mice, ferrets, hamsters, cats, and several species of nonhuman primates (cynomolgus and rhesus macaques, African green monkeys, and marmosets). MHV that infects both mice and rats often has been studied as a suitable model of human coronavirus diseases, according to Watanabe et al.[1].
Summary of Data
DeDiego et al.[2] challenged four groups of the transgenic mice intranasally with graded doses of rSARS-CoV and the survival was monitored for 13 days.
De Albuquerque et al.[3] inoculated A/J mice with MHV-1 intranasally via intranasal route and monitored the survival for 21 days.
References
- Citekey 1271 not found
- (2008). Pathogenicity of severe acute respiratory coronavirus deletion mutants in hACE-2 transgenic mice. Virology.. 376, 2.
- (2006). Murine Hepatitis Virus Strain 1 Produces a Clinically Relevant Model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in A/J Mice. Journal of Virology. 80, 21.
| ID | # of Doses | Agent Strain | Dose Units | Host type | Μodel | Optimized parameters | Response type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 260 | 4 | rSARS-CoV | PFU | mice hACE-2 | exponential |
k = 2.97E-03 LD50/ID50 = 2.33E+02 |
death | "Murine Hepatitis Virus Strain 1 Produces a Clinically Relevant Model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in A/J Mice." Journal of Virology. 80 (2006): 21. |
| 260, 261 | 0 | rSARS-CoV | PFU | mice hACE-2 and A/J | exponential |
k = 2.46E-03 LD50/ID50 = 2.82E+02 |
death | |
| 261 | 4 | MHV-1 | PFU | A/J mice | exponential |
k = 2.14E-03 LD50/ID50 = 3.24E+02 |
death | "Murine Hepatitis Virus Strain 1 Produces a Clinically Relevant Model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in A/J Mice." Journal of Virology. 80 (2006): 21. |
k = 2.97E-03
LD50/ID50 = 2.33E+02
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Parameter histogram for exponential model (uncertainty of the parameter)
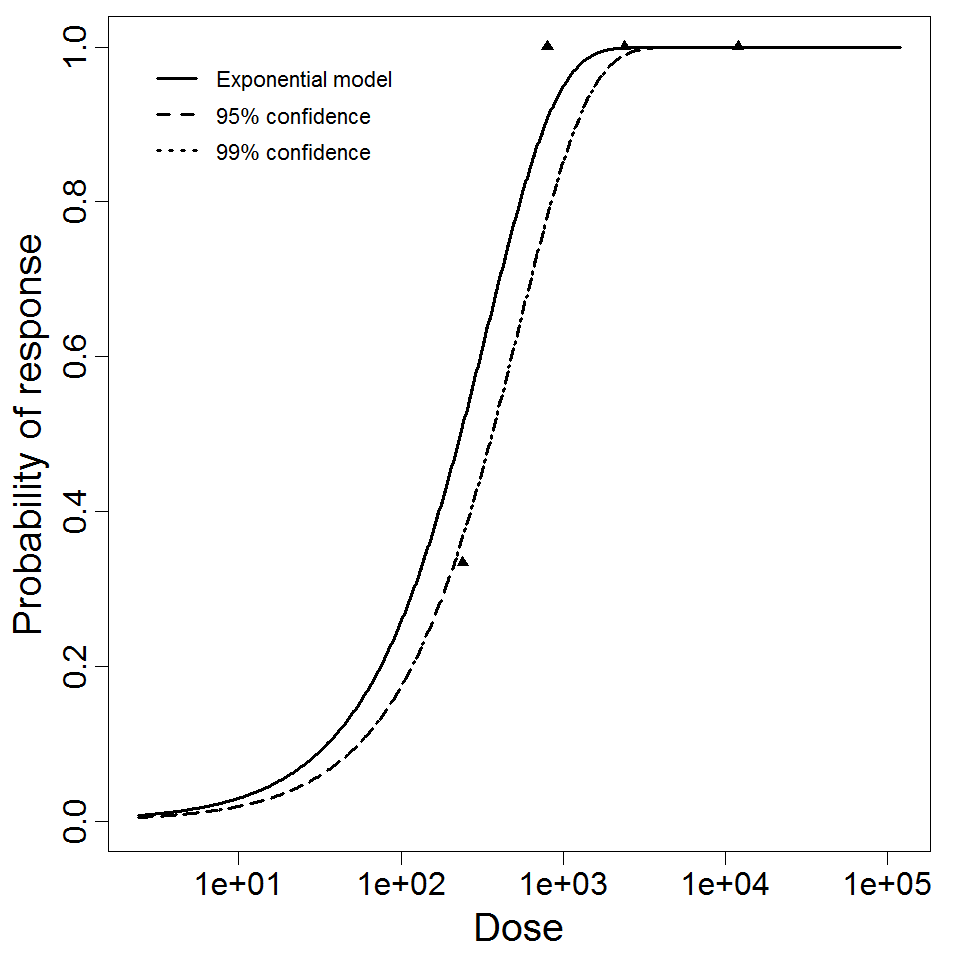
Exponential model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model
k = 2.46E-03
LD50/ID50 = 2.82E+02
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
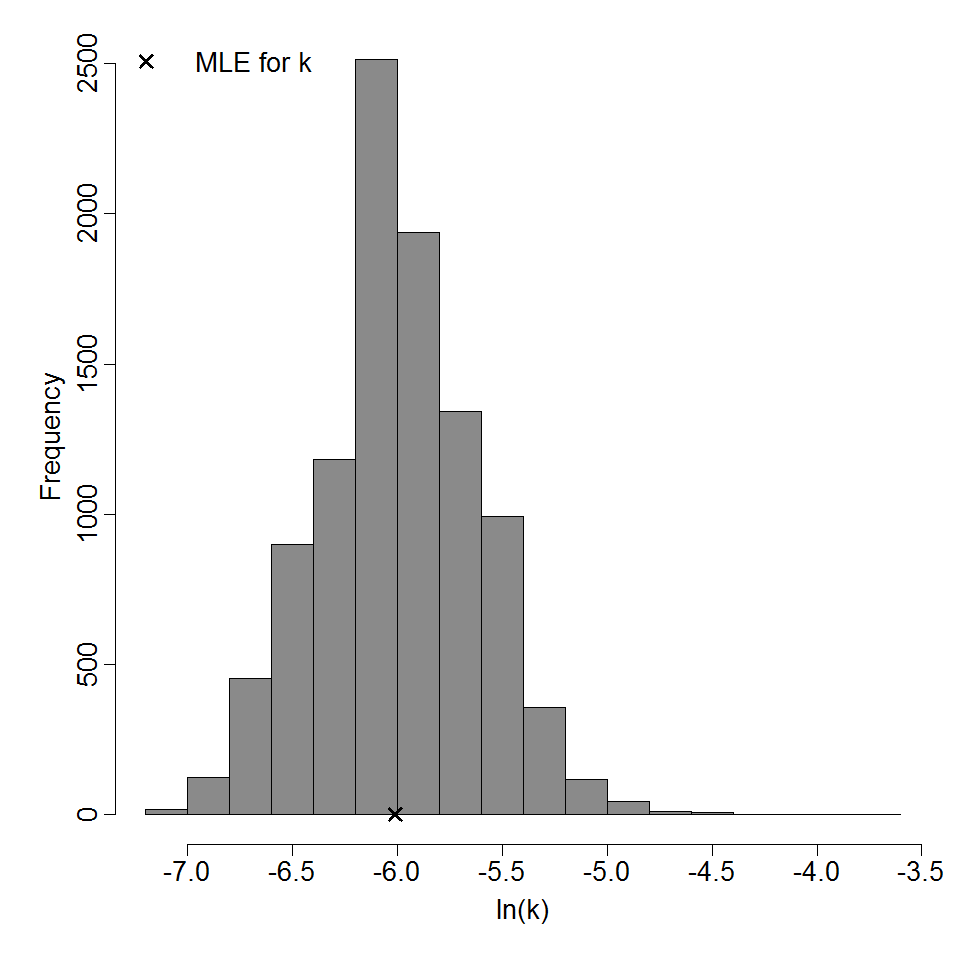
Parameter histogram for exponential model (uncertainty of the parameter)
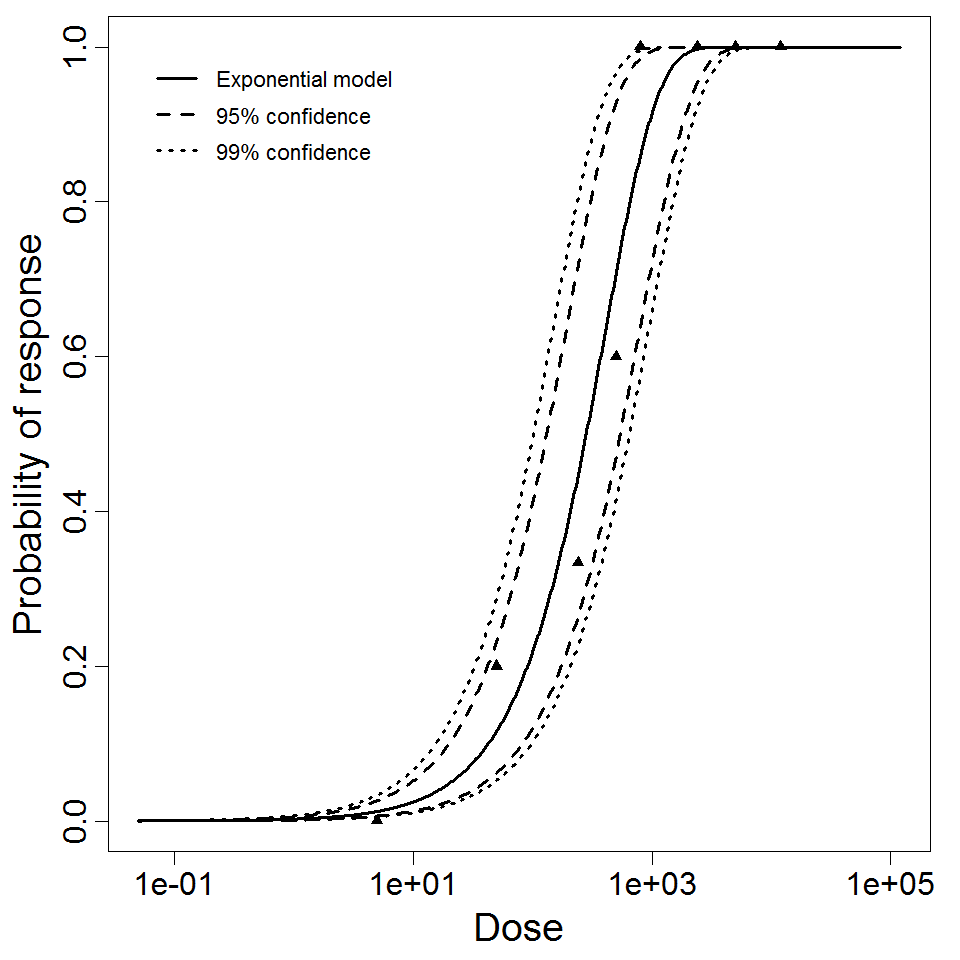
Exponential model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model
k = 2.14E-03
LD50/ID50 = 3.24E+02
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Parameter histogram for exponential model (uncertainty of the parameter)

Exponential model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model
 QMRA
QMRA