| Experiment ID |
Acanth_Intranasal4
|
|---|---|
| Agent Strain |
A. castellanii HN-3
|
| Contains Preferred Model |
No
|
| Reference |
Culbertson, C. ., Ensminger, P. ., & Overton, W. . (1966). Hartmannella (acanthamoeba). Experimental chronic, granulomatous brain infections produced by new isolates of low virulence. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 46, 305–314. |
| Exposure Route |
intranasal
|
| Response |
acute meningoencephalitis
|
| Host type |
mice
|
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of Doses |
3.00
|
||||||||||||||||
| Dose Units |
no of trophozoites
|
||||||||||||||||
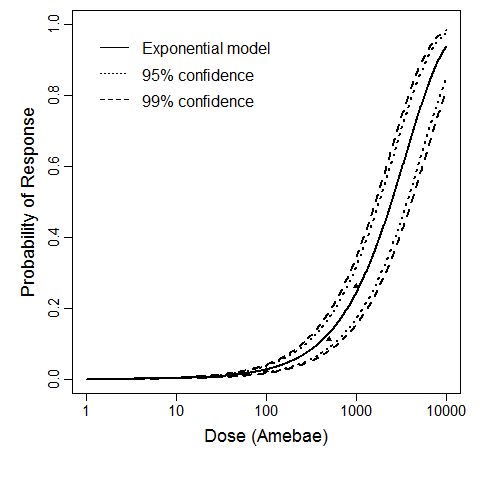
| Μodel |
exponential
|
||||||||||||||||
| k |
2.60E-04
|
||||||||||||||||
| LD50/ID50 |
2.67E+03
|
||||||||||||||||
| Experiment Dataset |
|
Culbertson et al. (1966) studied the pathogenicity of the HN-3 strain of A. castellanii (Culbertson et al., 1966; Marciano-Cabral & Cabral, 2003) on ether-anesthetized-specific-pathogen-free (SPF) mice. Cultures of amebae were grown in trypticase soy broth and diluted so that 0.03 mL of a concentrated suspension could be instilled intranasally into the mice by placing fluid over the nares (Culbertson et al., 1966; Culbertson, Ensminger, & Overton, 1965a; Culbertson, Ensminger, & Overton, 1965b).
The exponential model provided the best fit to the data.
Culbertson, C. G., Ensminger, P. W., & Overton, W. M. (1966). Hartmannella (Acanthamoeba): Experimental Chronic, Granulomatous Brain Infections Produced by New Isolates of Low Virulence. The American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 46(3), 305–314.