| Experiment ID |
242, 243
|
|---|---|
| Pathogen | |
| Agent Strain |
strain 74/81
|
| Contains Preferred Model |
No
|
| Reference |
Fitzgeorge, R. B., Baskerville, A. ., Broster, M. ., Hambleton, P. ., & Dennis, P. J. (1983). Aerosol infection of animals with strains of Legionella pneumophila of different virulence: comparison with intraperitoneal and intranasal routes of infection. Epidemiology & Infection, 90. |
| Exposure Route |
inhalation
|
| Response |
death
|
| Host type |
mice
|
|---|---|
| # of Doses |
9.00
|
| Dose Units |
CFU
|
| Μodel |
exponential
|
| k |
4.99E-05
|
| LD50/ID50 |
1.39E+04
|
Description
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
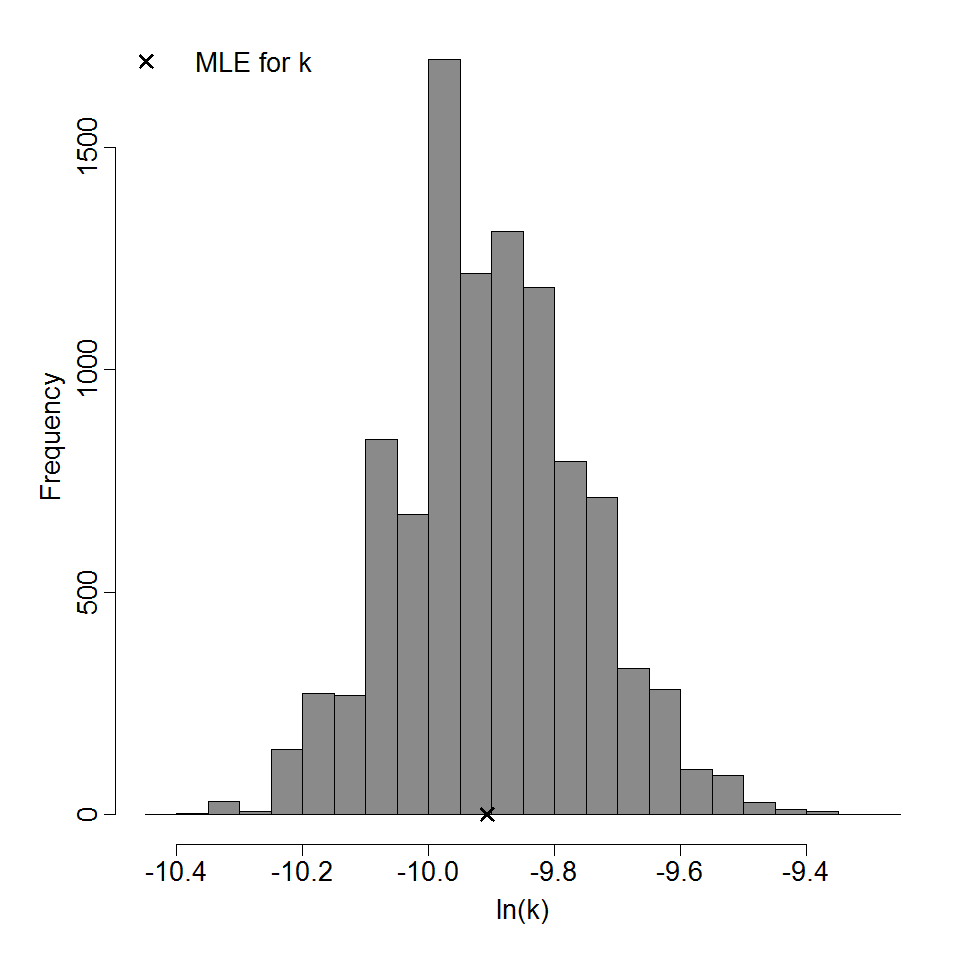
Parameter histogram for exponential model (uncertainty of the parameter)
Exponential model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model