| Experiment ID |
80
|
|---|---|
| Pathogen | |
| Agent Strain |
Quailes
|
| Contains Preferred Model |
No
|
| Reference |
Levine, M. M., DuPont, H. L., Formal, S. B., Hornick, R. B., Takeuchi, A. ., Gangarosa, E. J., … Libonati, J. P. (1973). Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) Dysentery. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 127, 3. |
| Exposure Route |
oral (in milk)
|
| Response |
disease
|
| Host type |
human
|
|---|---|
| # of Doses |
5.00
|
| Dose Units |
CFU
|
| Μodel |
beta-Poisson
|
| a |
2.03E-01
|
| N50 |
8.53E+05
|
| LD50/ID50 |
8.53E+05
|
Description
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
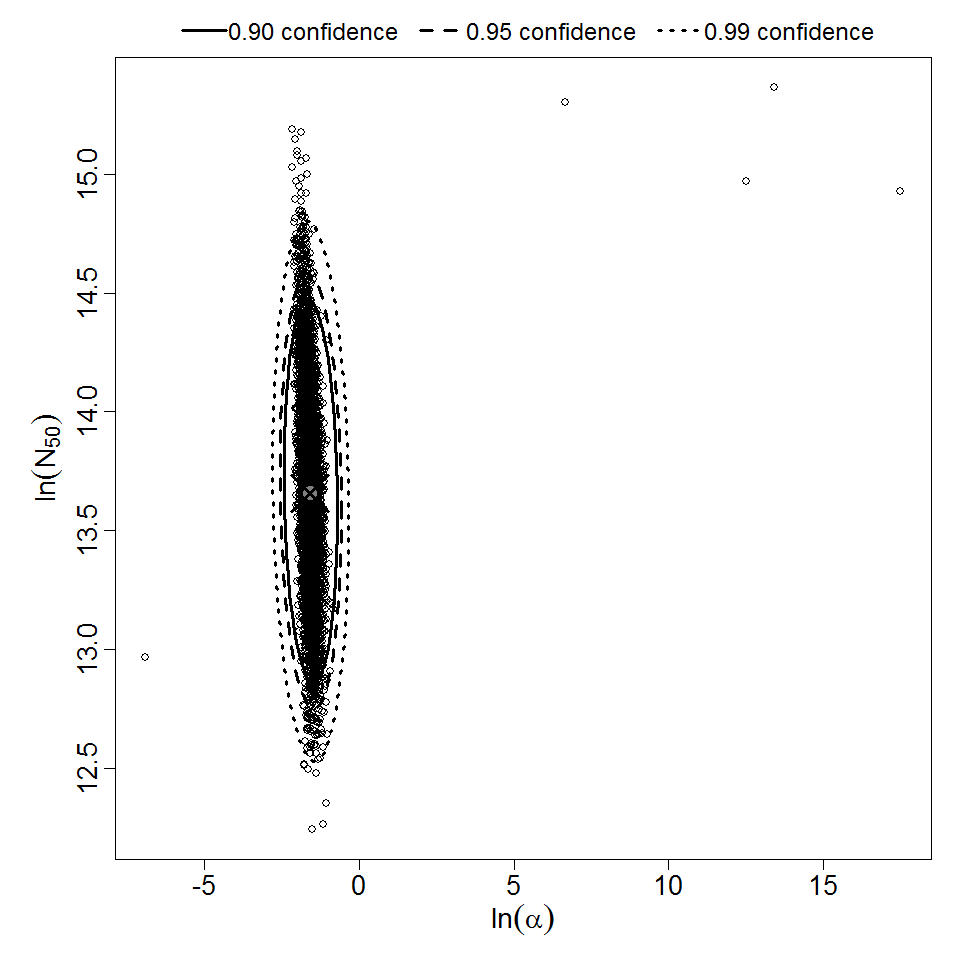
Parameter scatter plot for beta Poisson model ellipses signify the 0.9, 0.95 and 0.99 confidence of the parameters.
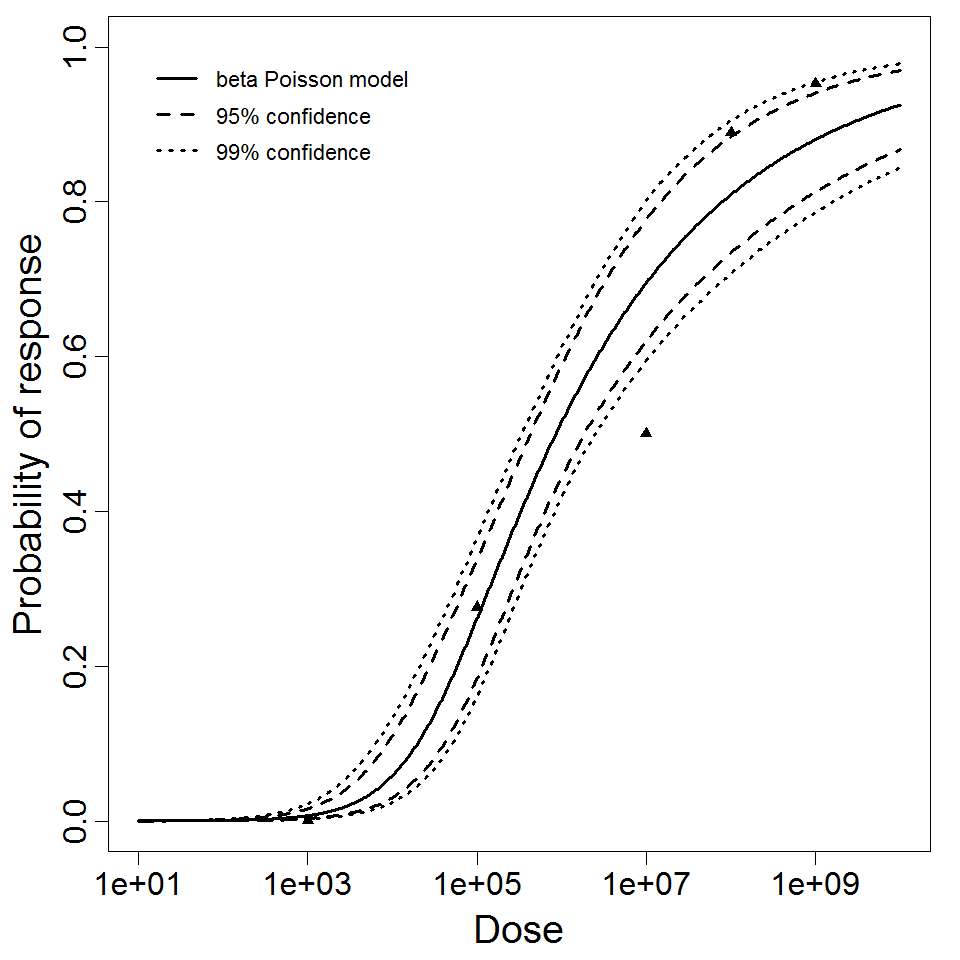
beta Poisson model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model