General Overview
Salmonella enterica serotype Newport is a gram-negative intracellular bacterium of considerable animal and public health concern. It causes significant clinical disease in livestock, particularly cattle, in humans, and in other animal species. Multiple antimicrobial resistant strains of Salmonella Newport have been recorded in the U.S. and Canada.
http://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/typhiTyphimurium-cantaloupe-08-12/
Summary Data
McCullough and Eisele orally inoculated human volunteers with S. Newport in 1951.
Recommended Model
Experiment number 235 is the only available model , hence it is the recommended model
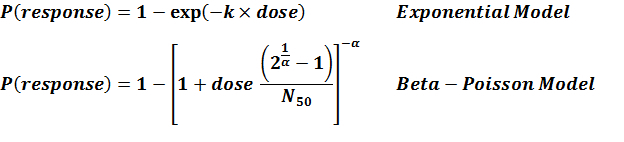
| ID | Exposure Route | # of Doses | Agent Strain | Dose Units | Host type | Μodel | LD50/ID50 | Optimized parameters | Response type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 235 | oral | 3.00 | *Salmonella newport* | CFU | human | exponential | 1.74E+05 | k = 3.97E-06 | infection |
McCullough, N. ., & Elsele, C. . (1951). Experimental Human Salmonellosis: I. Pathogenicity of Strains of Salmonella Meleagridis and Salmonella Anatum Obtained from Spray-Dried Whole Egg. Oxford Journal of Infectious Diseases, 88(3). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/88.3.278 |
Highest quality
Exposure Route:
oral
# of Doses:
3.00
Agent Strain:
*Salmonella newport*
Dose Units:
CFU
Host type:
human
Μodel:
exponential
LD50/ID50:
1.74E+05
Optimized parameters:
k = 3.97E-06
Response type:
infection
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Parameter histogram for exponential model (uncertainty of the parameter)

Exponential model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model