General Overview
Salmonella is a genus of rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-spore forming, predominantly motile enterobacteria . Many species of Salmonella have been isolated from eggs and egg products . Salmonella meleagridis is one of the most common serotype of Salmonella . Twenty human isolates of S. meleagridis had been identified in Canada so far during 1997.
http://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/
Summary Data
McCullough, and Eisele (1951) inoculated human volunteers orally with the S. Meleagridis strain I,II and III.
Recommended Model
Eexperiment number 238 is the recommended one as the strain I was more virulent than strain III.
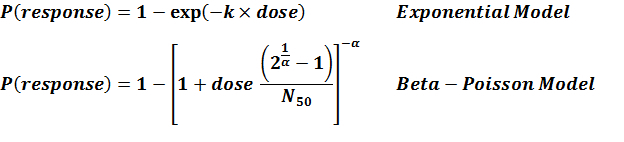
| ID | Exposure Route | # of Doses | Agent Strain | Dose Units | Host type | Μodel | LD50/ID50 | Optimized parameters | Response type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 238 | oral (with eggnog) | 11.00 | strain I | CFU | human | beta-Poisson | 1.68E+04 | a = 3.89E-01 N50 = 1.68E+04 | infection |
McCullough, N. ., & Elsele, C. . (1951). Experimental Human Salmonellosis: I. Pathogenicity of Strains of Salmonella Meleagridis and Salmonella Anatum Obtained from Spray-Dried Whole Egg. Oxford Journal of Infectious Diseases, 88(3). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/88.3.278 |
| 240 | oral (with eggnog) | 4.00 | strain III | CFU | human | beta-Poisson | 5.24E+05 | a = 8.85E-01 N50 = 5.24E+05 | infection |
Muller, D. ., Edwards, M. L., & Smith, D. W. (1983). Changes in Iron and Transferrin Levels and Body Temperature in Experimental Airborne Legionellosis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 147, 2. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/147.2.302 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameter scatter plot for beta Poisson model ellipses signify the 0.9, 0.95 and 0.99 confidence of the parameters.
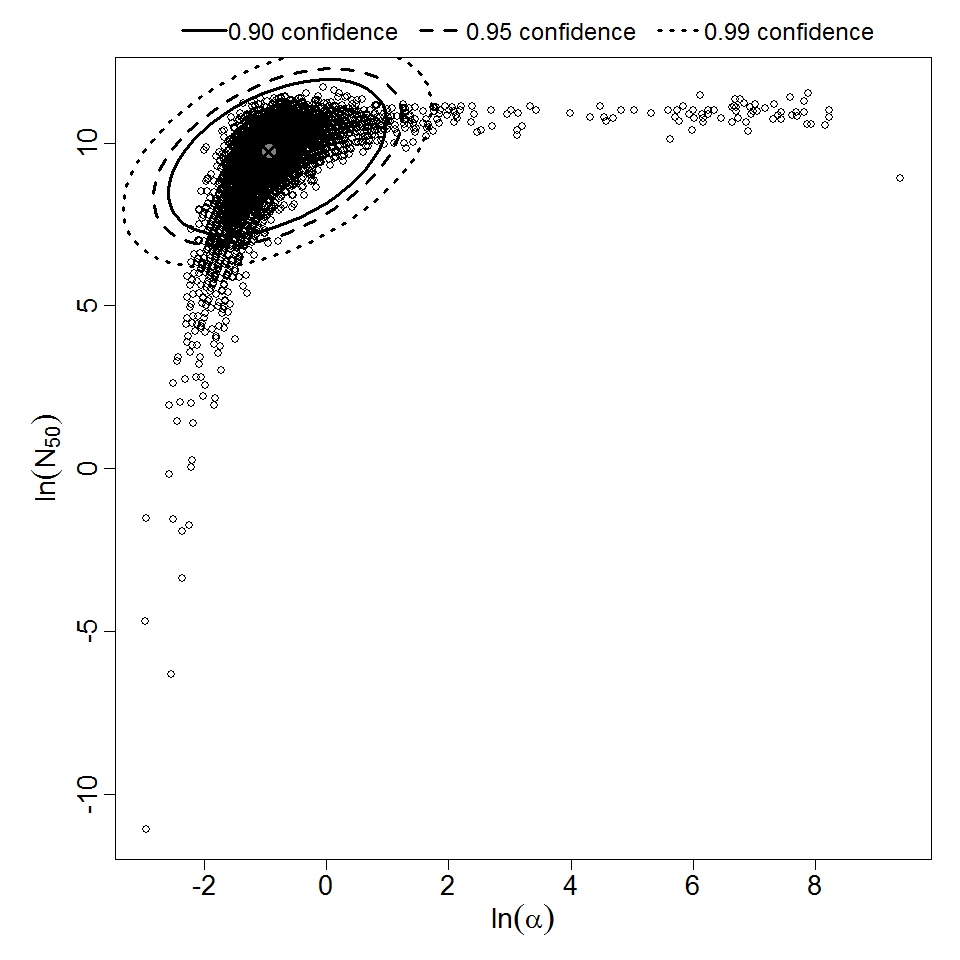
beta Poisson model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
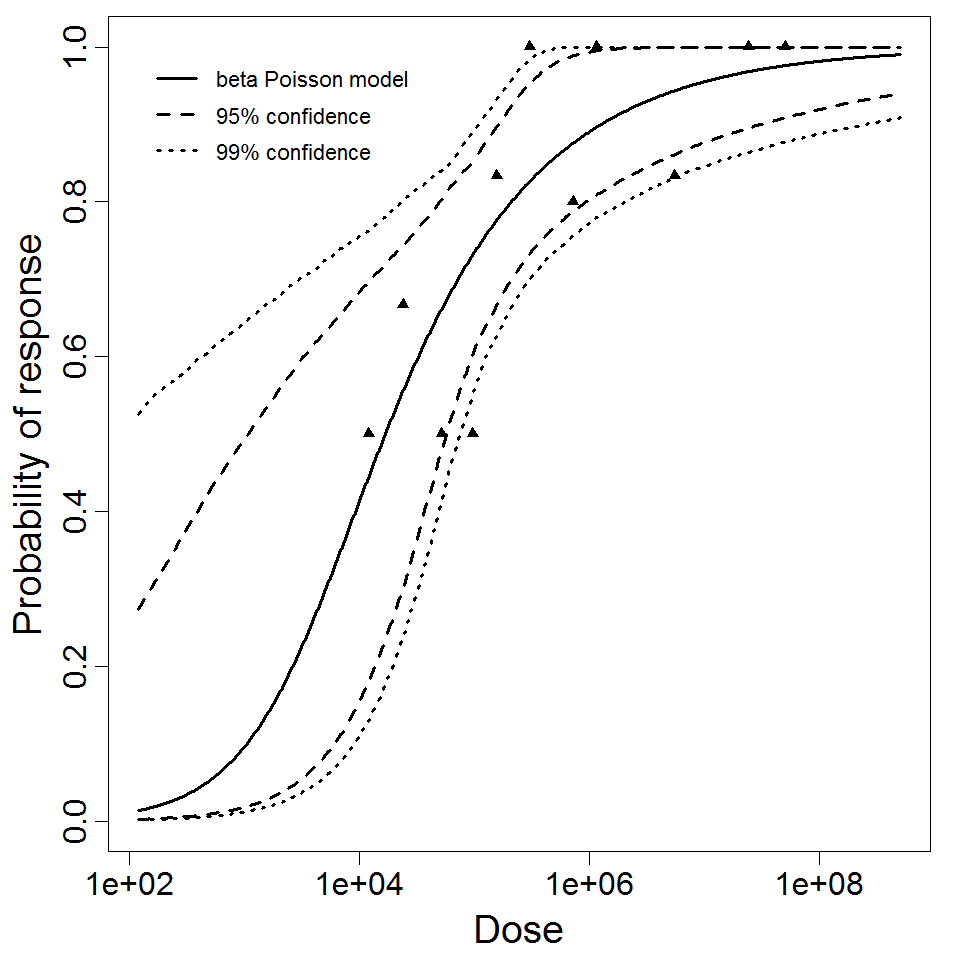
Parameter scatter plot for beta Poisson model ellipses signify the 0.9, 0.95 and 0.99 confidence of the parameters.

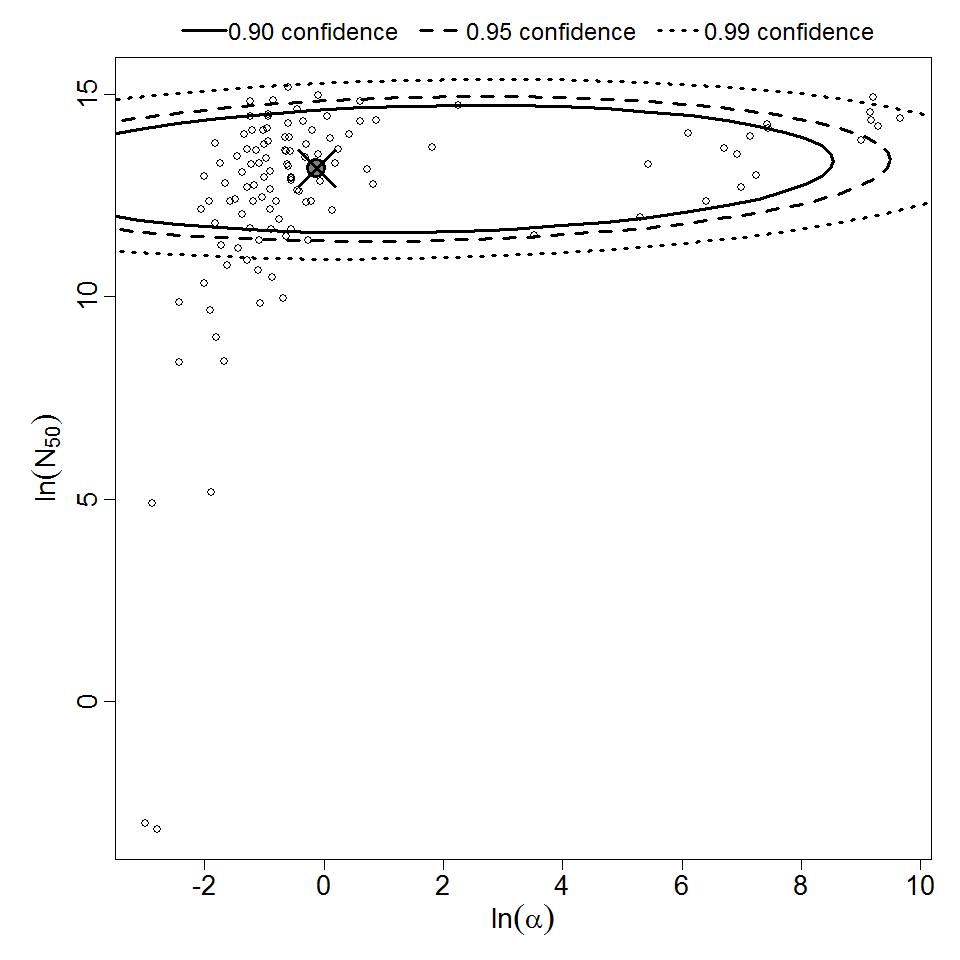
beta Poisson model plot, with confidence bounds around optimized model