Acanthamoeba: Dose Response Experiments (Cornea)
General overview
Acanthamoeba spp. are free-living amoeba (FLA) that have been commonly found in freshwater, tap water, and recreational water. Acanthamoeba spp.
| ID | Exposure Route | # of Doses | Agent Strain | Dose Units | Host type | Μodel | LD50/ID50 | Optimized parameters | Response type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acanth_Cornea1 | eyes-cornea | 4.00 | Acanthamoeba Ac118 | no of trophozoites | rat | exponential | 6,886 | k = 1.01E-04 | infection |
Badenoch, P. R., Johnson, A. M., Christy, P. E., & Coster, D. J. (1990). Pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba and Corynebacterium in the Rat Cornea. Archives of Ophthalmology, 108, 1. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/638228 |
| Acanth_Cornea2 | eyes-cornea | 4.00 | Acanthamoeba Ac118 | no of trophozoites | rat | exponential | 1.91E+03 | k = 3.63E-04 | infection |
Badenoch, P. R., Johnson, A. M., Christy, P. E., & Coster, D. J. (1990). Pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba and Corynebacterium in the Rat Cornea. Archives of Ophthalmology, 108, 1. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/638228 |
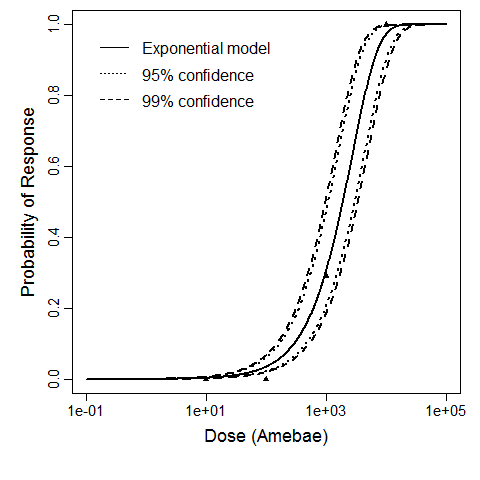
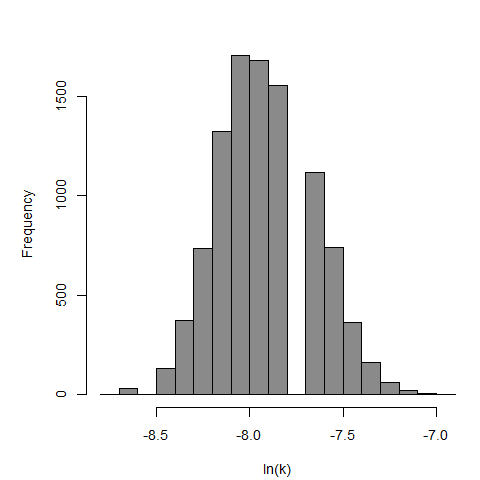
Badenoch et al. (1990) studied the combined effect of Acanthamoeba Ac118 (a group III isolate) and the bacterium Corynebacterium xerosis on the corneas of female Porton rats. A constant dose of 104 C. xerosis with increasing doses of Acanthamoeba spp. were injected into incisions in the rat corneas using a microsyringe (Badenoch et al. 1990).
The exponential model provided the best fit to the data.
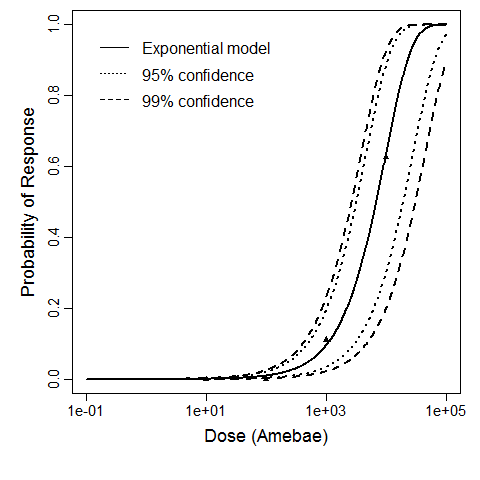
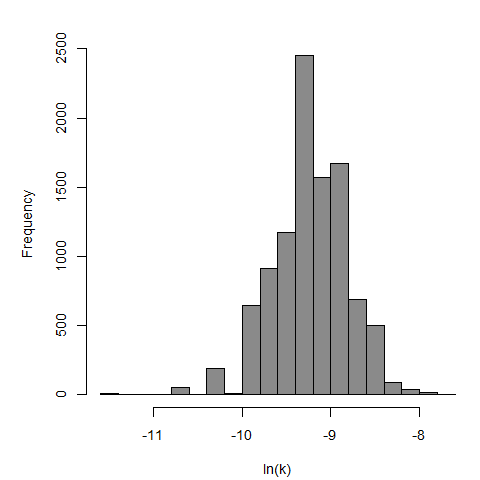
Badenoch et al. (1990) studied the combined effect of Acanthamoeba Ac118 (a group III isolate) and the bacterium Corynebacterium xerosis on the corneas of female Portion rats. A constant dose of 106 C. xerosis with increasing doses of Acanthamoeba spp. were injected into incisions in the rat corneas using a microsyringe.
The exponential model provided the best fit to the data.
Badenoch et al. (1990) studied the combined effect of Acanthamoeba Ac118 (a group III isolate) and the bacterium Corynebacterium xerosis on the corneas of female Porton rats. A constant dose of 104 C. xerosis with increasing doses of Acanthamoeba spp. were injected into incisions in the rat corneas using a microsyringe (Badenoch et al. 1990).
The exponential model provided the best fit to the data.
| Dose (no. of organisms) | Positive Responses | Negative Responses | Total Subjects/Responses | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0 | 8 | 8 | |
| 100 | 0 | 16 | 16 | |
| 1000 | 2 | 16 | 18 | |
| 10000 | 5 | 3 | 8 |